an open-source orchestration library that helps developers connection LLMs for building complex applications_
![[Pasted image 202509117.png.webp]]
It provides a standard interface for various components and abstractions:
LLMs: The backbone of LangChain, LLMs like OpenAI’s GPT-3 or GPT-4 provide the core capabilities for understanding and generating language. They are trained on vast datasets to produce coherent and contextually relevant text.Prompt Templates: These templates structure the input to LLMs, maximizing their effectiveness in understanding and responding to queries. By designing effective prompts, developers can guide the LLMs to produce desired outputs.Output Parsers: These components refine the language generated by LLMs into formats that are useful and relevant to specific tasks, enhancing the overall user experience.Vector Store: This component handles the embedding of words or phrases into numerical vectors, which is essential for tasks involving semantic analysis and understanding language nuances.Agents: Agents are decision-making components that determine the best course of action based on input, context, and available resources. They enable LLMs to interact intelligently with their environment.
Chain#
Chain of Thought (CoT), the implementation on minimum manageable steps
- explicitly guiding the LLM to think step-by-step through a problem
- split the overall task into subtasks and run the subtasks sequentially
- the output of one step becomes the input of the next
![[Pasted image 202509118.png.webp]]
chain = prompt | model **|** outputParser
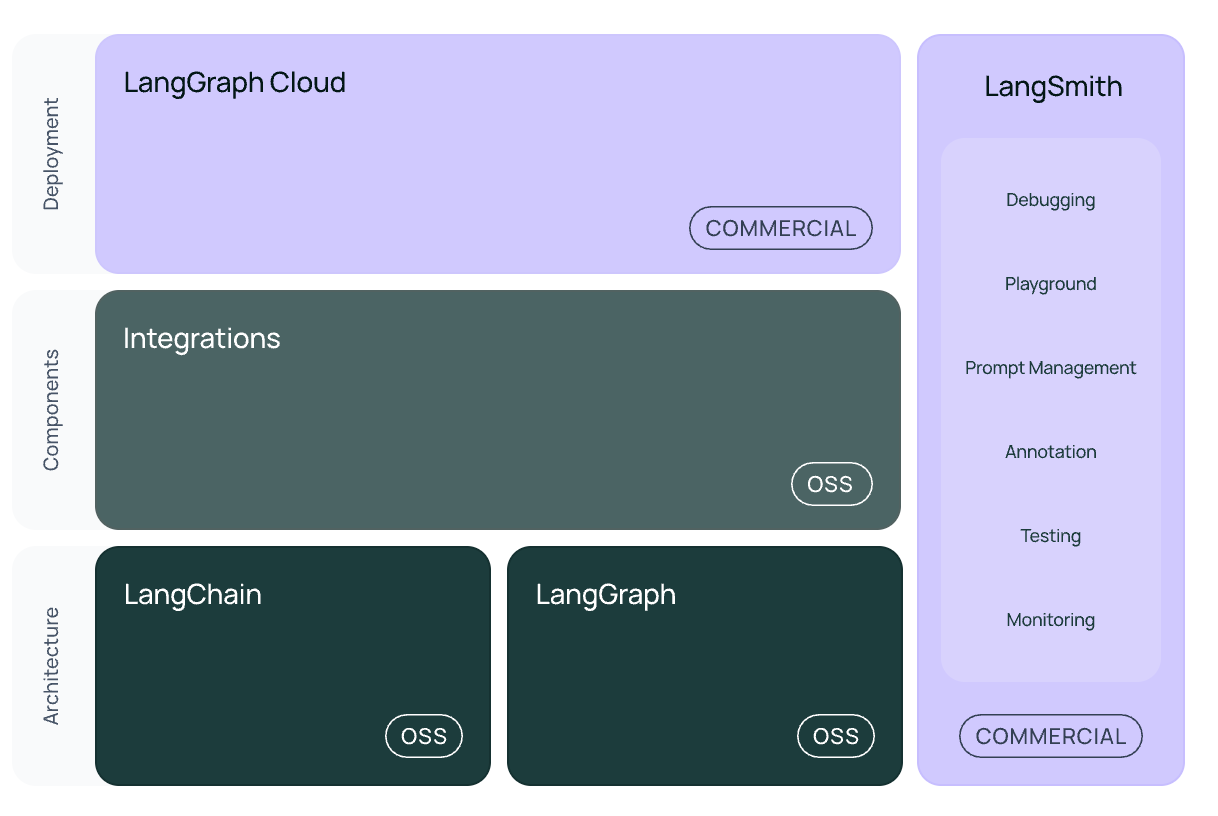
LangChain Ecosystem#
!
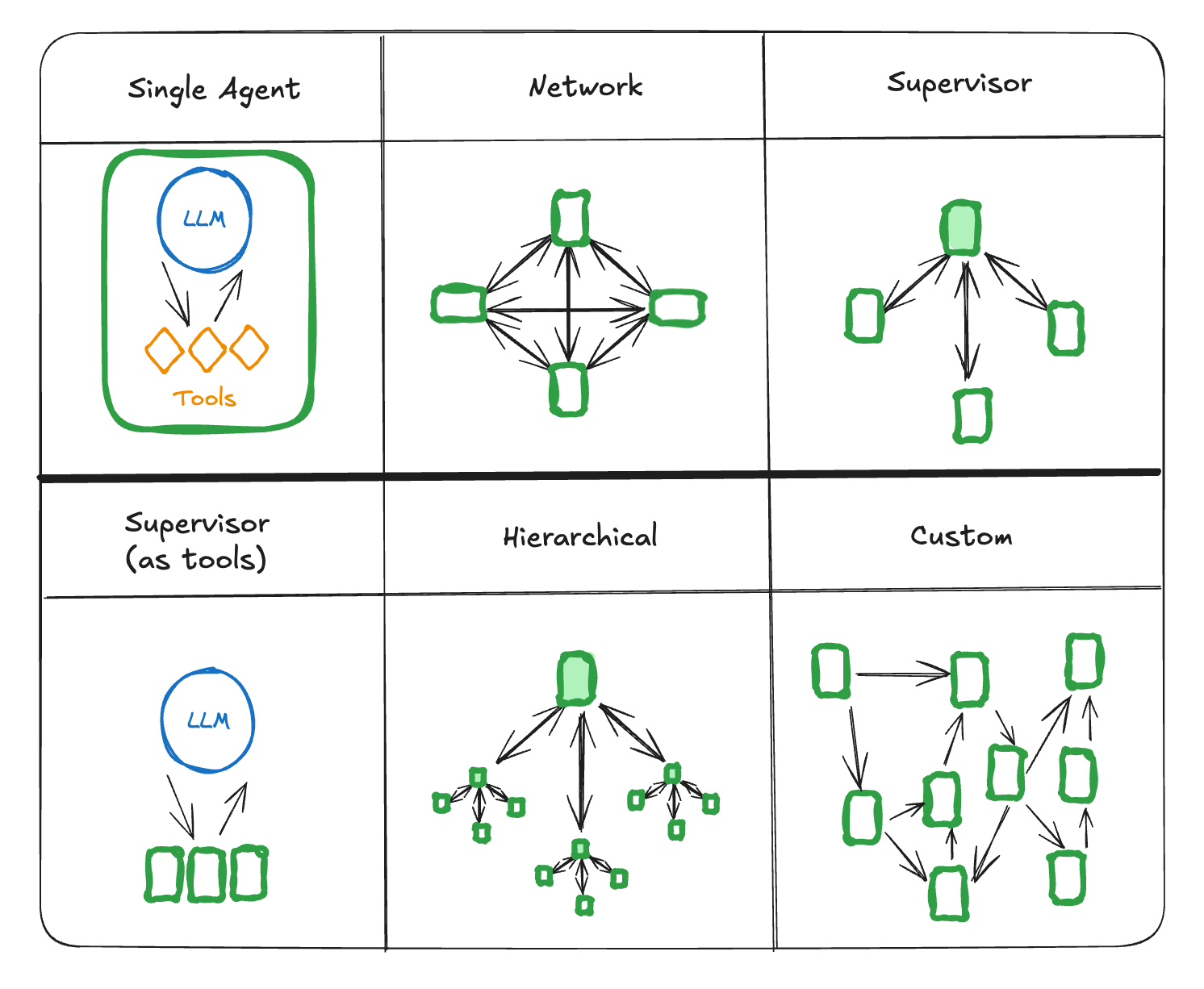
LangGraph#
LangGraph is an extension of LangChain that focuses on building more complex and controllable agent workflows using a graph-based approach
LangChain vs LangGraph (DAG vs Graph)#
!
Key components:
State: A shared data structure that represents the current snapshot of your application.Nodes: Python functions that encode the logic of your agents. They receive the currentStateas input, perform some computation or side-effect, and return an updatedState.Edges: Python functions that determine whichNodeto execute next based on the currentState. They can be conditional branches or fixed transitions.
Support cases such as time travel/human in the loop/parallelization/multi agents(stateful) architecture
Deciding Between LangChain and OpenAI API#
Use Direct API (such as OpenAI) When:#
-
Simplicity and performance are top priorities.
-
Tasks are straightforward and don’t require chaining operations.
-
Answering single-turn questions
-
Running one-off analyses
-
Performance-critical applications
Use LangChain When:#
-
You need to chain multiple operations conveniently.
-
Development speed and maintainability are important.
-
Your project involves integrating tools, external APIs, or maintaining state across interactions.
-
Ease of Chaining Tasks: You can easily combine multiple operations (e.g., answering questions based on external data).
-
Built-in Tools and Agents: LangChain offers agents to manage complex workflows with minimal code.
-
Extensibility: It integrates with external systems like document stores, APIs, and Python functions.
LangSmith#
![[Pasted image 2025091111.png.gif]]
Appendix#
- https://medium.com/@ab.hassanein/demystifying-langchain-tool-calling-agent-75cba2c46a61
- https://langchain-ai.github.io/langgraph/concepts/low_level/#graphs
- https://blogs.adityabh.is-a.dev/posts/langchain-vs-openai-simplicity-vs-scalability/
- https://www.pinecone.io/learn/series/rag/rerankers/
!